Friday, September 26, 2008
ArchiCulture Cafe number TEN
Considering the images included in the presentation, I'm assuming that the level of architectural adornment throughout this country is high and intricate. The images showed geometric patterns littering the walls of native architecture in stark, bright colours which I found I somehow knew instinctively were definitive of the native South African culture. This instinctive perception of cultural iconic imagery made me think about cultural icons and the description of the struggle between black people and white people in this country made me think of the owners of these cultural icons. Of coures, I thought, the black native people who originally occupied the land are the true owners of these beautiful iconic adornments. Then this thought led me on to think of the question "do cultural icons have owners at all?" as well as "when there are two seperate origins of cultural beginning present in the one country, how does the culture that is formed by both origins combined define itself in a way that appeases both origins?"
When considering the first question, I found the concept of owning a cultural icon initially repulsive. Although cultures are made up of groups of individual people, the icons that form the cultural identity could surely not be owned by any one person but instead owned by all people of that culture simultaneously. The concept of ownership pulled images into my head of money, trade and property but immediately after an image of a person saying the words "my country" appeared.
When considering the second question, I was immediately struck by the complexity of it as well as the similarity to Australian and Indigenous cultures. I can't pretend that I know the answer to this question - perhaps it can't be answered because of all the variables and circumstancial elements. But upon contemplating both the South African and Australian histories and their possessions of violence and oppression, I came to speculate that maybe the culture that is formed by both origins combined will never be as sound, rich and steady as the two seperate origins individually. This thought made me a little bit sad.
The case study illustrated in the presentation described the Red Location Museum in New Brighton, Port Elizabeth. The existence of 'illegal' shanty towns in this location provided the main spark for the design of the Museum. These shanty towns were the dwellings of people who were shut out as a result of cultural-origin-conflict. The accommodations in these towns were insufficient and laced with poverty, labour and individual strivings. In addition to these shanty towns, the factories in which most of the shanty-town-dwellers obtained meager earnings were also extracted as part of the design for the Museum.
I found it beautiful the way the architect had decided to use the materials which formed the most difficult and strenuous environments these people encountered. The materials, usually associated with destitute circumstances, were transformed into a symbol of cultural strength through a change in context. Here, the architecture not only helped to acknowledge the unsatisfactory circumstances in which these people lived, but it also helped to strengthen the collective people in their views and actions. Through recognition and encouragement in the form of the museum the people of this culture were empowered.
Wednesday, September 17, 2008
ArchiCulture Cafe number NINE
When I was studying art and art history, it was often stated that artists are social commentators who translate the practices of their culture back to the public through the lens of their formulated opinion. If an artist makes an artwork which is to be displayed publicly and which comments positively on the culture of the site in which it is placed, it is suggested that outsiders and onlookers are more likely to respond positively to that site.
Not only outsiders and onlookers but local people could benefit from such an installation. As mentioned in the lecture, a piece of public art would ameliorate the area in which it is placed in a number of ways. Most of these ways were of benefit to the larger macro environment such as economy, employment rates and tourism. But on a smaller level, benefits could be as simple as making the workplace of local individuals more aesthetically pleasing and therefore less depressing.
In addition to the micro-level benefits of lifting workplace depression, it was stated in the lecture that public art provides jobs for artists and artsworkers. During the second (and my last) year of my art degree, the concern of becoming a poor, part-time-worker-part-time-artist was commonplace. The passion for art was not diminished for most by this looming probability but the preference, of course, was to work for art and with art on the whole. If public art, then, is providing jobs for artists, and artists could be described as social commentators, the cycle has the potential to have perpetual and very positive results.
The cyclical nature of this relationship between artists and public art is reminiscent for me of the cyclical nature of culture and architecture. Public art is the product of the work of an individual (the artist) and because it has come from that individual it represents a part of their identity. But because it is part of a public environment, it also influences the outside people who interact with, move past and look at it. Similarly to this, architecture is the product of the work of an individual (the architect) and because it has come from that individual is represents a part of their identity. But because it is part of a public environment, as well as being able to be inhabited or worked in, it also influences the lives and experiences of outside people.
Thursday, September 11, 2008
ArchiCulture Cafe number EIGHT
In addition to finding these things, I also found that the artwork was presented here as a 'bad' thing. While in informing (and/or designing) it would probably be best to stick to the ideals of design, I tend to think it probably wouldn't harm anyone to add elements of art to a design proposal - but only where it adheres to the design commandments of course.
The rest of the lecture I found highly useful and I intend to keep a copy to refer to in future when creating design presentations. Even though the ideas and instructions presented are usually considered in design presentation, I found it helpful for them to be layed out in an order (designed ?) and articulated in such a way as to be easily accessible by all.
Saturday, September 6, 2008
ArchiCulture Cafe number SEVEN
The first was the idea that place consists of a great number of aspects (like culture!) and that the consideration of the place involved with architectural and design interventions is paramount to the overall meaning of the finished product. The cognitive and sensory experiences of the user of a space makes up their understanding of the place of a design outcome even before they enter the site - at the very least cultural ideologies and events attached to the location and details of a site will inform a user's idea of the type of experience they are to have there. Kelly explored this, mentioning experiential aspects such as social, historical and territorial associations that could be attached to specific places.
The second was the idea that the traditional and historical aspects and the contemporary aspects of a cultural group may not necessarily link together in a way that is obvious or conducive to an uncomplicated manifestation of cultural practices that may have been easy in the past. The example given was the iconic images of contemporary Brisbane and Indigenous identity. The apparently disjointed relationship between these two identities presents, to me, a number of stimulating prospects for architectural interventions.
The third was the fact that cultures change over time with progressions of technology and liberal social shifts. As a designer, it would be important to know which practices, objects and concepts of a particular culture are contemporary and which are historical. The use of cultural aspects which come from a certain time period could hold local meaning which contradict the conceptual intent of a particular design proposal.
The fourth is the idea of place changing meaning through the translation between Indigenous and non-Indigenous occupation. The meaning associated with Indigenous historical occupations of a particular site may be starkly contradictory to the meaning associated with non-Indigenous site proposals or existing buildings. I tend to think it would be extremely difficult to appease both sides of this dichotomy with so many cultural aspects to consider.
Following on from this idea of conflicting meanings in place, I found the Inala example was very interesting in that it started as a predominantly non-Indigenous site and now has a very strong Indigenous population. It was fascinating to consider that some of the Inala Indigenous population presented in the lecture formed a resolute connection to the site of their current dwellings. Attaching this meaning to a contemporary site which might not necessarily hold an historical link with Indigenous culture suggests to me a site-specific aspect of Indigenous culture. This site-specific importance is extremely fascinating to me as a designer as it could provide a rich amount of material for design solutions.
Thursday, August 28, 2008
ArchiCulture Cafe number SIX
It was eye opening to me to realise the complexity of the difficulties which can arise when dealing with a particular cultural group. Of course there are obstacles to tackle when working with any design brief but the issues and problems that were detailed by Carroll seemed a bit nightmarish to me. Having said this, I would have relished working on such a rich and complex design challenge. Collaboration with the Indigenous people as well as having to consult with the other cultural groups on the site would be a very interesting process and would provide an amount of frustration. However, I tend to think that solving the causes of this frustration would result in a rewarding outcome. The fact that you would have to solve the causes before the building could be built is being put aside for this reflection.
Also dealing with a committee of Indigenous people who are not the traditional owners of the site would mean that the set of boundaries, requirements and things to consider would be completely different to if you were dealing with the traditional owners. It strikes me as odd that the committee wouldn't have any traditional owners and if this was the case, then would that mean that the traditional owners would be opposed to anything built on the site?
This complexly woven fabric of difficulties and issues makes me consider the question of the interdependent relationship between architecture and culture. The amount of boundaries and concepts to adhere to with regard to this site and design brief seems ostensibly to feed only one side of the relationship - the cultural group has already been defined by centuries of existence and is now defining this architectural outcome, without informing further the definition of the cultural group. However, as a result of digging deeper in my brain, the thought arose that the Indigenous peoples rely on gathering and family groups as a main defining concept and that the site would help to redefine the way these gatherings and family groups come together in contemporary times.
Which leads me on to a concept presented in the reading Contested Sites of Identity and the Cult of the New by Kylie Message. The "juggling of tradition and modernity" makes me think of this idea of bringing traditional practices to a contemporary setting. In addition to this similarity, I noticed that the Centre Culturel Tjibaou draws on cultural aspects to inform its materials and conceptual framework. This makes me think of the question if the architectural result has been designed by persons outside the cultural group, can it really be considered architecture from that particular cultural group?
The other aspect of the reading I found of note was the description of Jean-Marie Tjibaou's cultural philosophy. His ideas that the Kanak people should not become "black Frenchmen" but instead define themselves seperately from the French - holding a 'self-confident identity rooted in culture and history'. To me it seems that these ideas have a parallel nature to the Australian Indigenous peoples and therefore the architecture which arises from this particular cultural group (and any person of European descent who wishes to design for the Indigenous people) would form part of the continuous redefinition of contemporary Indigenous peoples.
Thursday, August 21, 2008
Archi Culture Cafe NUMBER FIVE
This week we were given a lecture by Anoma Kumarasuriyar on the Japanese art of Tea and Tea Houses. I found it endlessly interesting and was captivated by how such practical aspects of the cultural architecture contributed to the elements of the Tea House.
From listening to this I took away a few key points that hit me square in the chest:
- Something happens, then something else happens and in between them you experience the space. If nothing happens, then there is a void.
- The concept of impermanent, imperfect, incomplete
- The reduction of the movements of the body to only the essential
For the tutorial exercises our group had to create two mind maps: one capturing the Tea House and its aspects and one capturing our proposed assignment topic and its aspects.
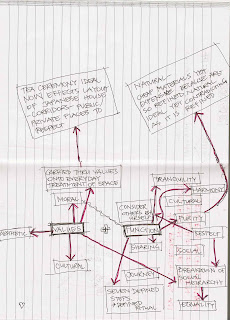
This first mind map is describing the Tea House - breaking it down into elements of its design that stem from cultural values and functions.
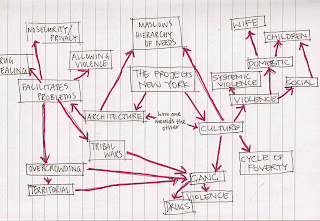 This mind map outlines the aspects of our proposed assignment topic (the Public Housing Projects in New York City).
This mind map outlines the aspects of our proposed assignment topic (the Public Housing Projects in New York City).The mind maps were a really useful tool for visualising a topic. They set out the concept for analytical consideration. They are also good as conceptual platforms from which to grab other elements of the topic which you perhaps wouldn't have thought of without being able to see the links between existing elements of the concept.
From the mind map that my group created for the assignment topic, we were able to extract a more concise way of describing our topic - which will help in our research along the way.
It was
Archi Culture Cafe NUMBER THREE
- Design theory and Design understanding and the crossing of cultures of architects / designers / users and clients
- The designer must "maintain a commitment to openness and difference" and make an effort towards "understanding a country's culture and practices"
- Professional values are defined by the education and values of the field
- Clients and users assume that their values will be accommodated in the end result. Sometimes these don't match with the designer's values. This may lead to the viewing of a client as "uneducated" in the design language
- A design project could be rated according to its reviews by other designers, as opposed to the level of client satisfaction, both now and in the long term. -> Design inconsistencies or client satisfaction!?
- ALIGNING VALUES: a complex web of human dynamics are fundamental to design decision making
-> social aspects of design - MASLOWS HEIRARCHY OF NEEDS is a good thing to consider in relation to this
- The values that you hold as a designer in practice will contribute to the selection process of clients and users when selecting designers to hire - a particular set of values that draw a client to you as a designer
- Use participatory methods of designing and have a sensitivity to the cultural as the soul of design.
Culture is a CAVE
- Some elements are visible immediately and from the outside.
- The deeper you delve the more information you will receive.
- There are many different aspects - this shows how culture, although it seems like it from the outside, isn't one element or phenomenon but rather a collection of ideas, actions, morals, etc, that collaboratively contribute to culture. To understand a culture, its 'avenues' have to be understood.
- To explore a cave a light is needed. In terms of culture, the light is like the knowledge gained from your explorations into the various aspects of a particular culture.
Whether by immersion or research, delving into a culture would inevitably teach you more about a culture. The thing about the cave is that you have to be brave enough to walk in, taking the risk that something hairy might jump out at you. Not that something hairy will jump out at you from a culture or its aspects, but I think this risk taking is kind of like being willing to understand a way of thinking or living that is different to what you are used to.
Culture is a HUMAN BODY
- Sums of the parts contribute to the running of the whole
- The organs each have their own value, but the body can not function without all of them working and functioning simultaneously
- Some parts may seem more prominent than others but still could not function as individual units
This metaphor is interesting because of the way I understand the aspects of culture to work with each other. Like I mentioned in a previous post, the relationship between architecture and culture is cyclical - one aspect bears a reason for existing because another aspect came into being due to yet another. Then marking this up against the human body metaphor, for example the veins don't have a reason for existing without blood - which translates to one aspect/function of culture not existing without another.
Culture is a TREE
- The roots are like cultures historical beginnings and precedents
- Age rings are layers upon layers of growth and added richness
- The trunk is like the culture as a whole - what everything stands upon
- The branches are the breaking up of the trunk/culture into smaller parts, this is where they are understood
- The tree continues to grow and change - both from internal and external influences
I like this metaphor because it makes reference to the history of a culture. Similar to the human body metaphor, a culture couldn't exist without an origin or a history. Also I like the tree because it refers to evolution and the constant alive-ness of a culture - how it moves and grows with the ages and gathers aspects along the way (layers in its trunk).
In this tutorial we had to hand in a personality survey that we were given in the last session, which focused on our personalities with regard to roles in a team. My results told me that as my primary role I am the Implementer and my secondary role is the Plant. The implementer is someone who mediates and provides direction for research and avenues to take in sticky sitches. The plant is someone who is often off with the fairies and unreliable but who comes up with awesome plans and ideas. I think I vary between both, probably if I'm being truthful I tend to be the unreliable plant more, but I am glad that mostly I can be seen as the Implementer and I will try my hardest to make this the whole case in the future.
The make up of my group consisted of (I think) three Implementers, one Finisher and one Coordinator. Pretty sweet.